本文简要介绍了Code的基础概念以及简单解释应用。
快排
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public static void quickSort ( int a , int l , int r ) {
if ( l >= r ) return ;
int x = a [ l + r >> 1 ] , i = l - 1 , j = r + 1 ;
while ( i < j ) {
while ( a [++ i ] < x ) ;
while ( a [-- j ] > x ) ;
if ( i < j ) {
int t = a [ i ] ;
a [ i ] = a [ j ] ;
a [ j ] = t ;
}
}
quickSort ( 1 , j );
quickSort ( j + 1 , r );
/*
quickSort(1, i - 1);
quickSort(i, r);
*/
}
归并
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public static void mergeSort ( int a , int l , int r ) {
if ( l >= r ) return ;
int mid = l + r >> 1 ; // l + (r - l) / 2
mergeSort ( l , mid );
mergeSort ( mid + 1 , r );
int k = 0 , i = l , j = mid + 1 ;
while ( i <= mid && j <= r ) {
if ( a [ i ] <= a [ j ] ) temp [ k ++] = temp [ i ++] ;
else temp [ k ++] = temp [ j ++] ;
}
while ( i <= mid ) temp [ k ++] = a [ i ++] ;
while ( j <= r ) temp [ k ++] = a [ j ++] ;
for ( int i = l , j = 0 ; i <= r ; i ++ , j ++ ) {
a [ i ] = temp [ j ] ;
}
}
冒泡
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public static void BubbleSort ( int a , int n ) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 1 ; j < n - i ; j ++ ) {
if ( a [ j - 1 ] > a [ j ] ) {
int t = a [ j - 1 ] ;
a [ j - 1 ] = a [ j ] ;
a [ j ] = t ;
}
}
}
}
// 优化
public static void BubbleSort ( int a , int n ) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) {
int exchange = 0 ;
for ( int j = 1 ; j < n - i ; j ++ ) {
if ( a [ j - 1 ] > a [ j ] ) {
int t = a [ j - 1 ] ;
a [ j - 1 ] = a [ j ] ;
a [ j ] = t ;
exchange = 1 ;
}
}
if ( exchange == 0 ) break ; // 代表已经有序
}
}
二分
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// 寻找x
int l = 0 , r = n - 1 ;
// 左边界
while ( l < r ) {
int mid = l + r >> 1 ;
if ( a [ mid ] >= x ) r = mid ;
else l = mid + 1 ;
}
// 右边界
int l = 0 , r = n - 1 ;
while ( l < r ) {
int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1 ;
if ( a [ mid ] <= x ) l = mid ;
else r = mid - 1 ;
}
// 加=表示寻找小于等于mid的最后一个元素
// 不加=表示寻找小于mid的最后一个元素
BigInteger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public BigInteger ( String val )
add
subtract
multiply
divide
mod / remainder
max
min
divideAndRemainder // 返回一个数组[商, 余数]
BigInteger bi1 = new BigInteger ( "61893691328915" );
BigInteger bi2 = new BigInteger ( "1234354654424" );
bi2 . add ( bi1 );
bi2 . subtract ( bi1 );
bi2 . multiply ( bi1 );
bi2 . divide ( bi1 );
bi2 . mod ( bi1 );
bi2 . max ( bi1 );
bi2 . min ( bi1 );
bi2 . divideAndRemainder ( bi1 );
BigDecimal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public BigDecimal ( double val )
public BigDecimal ( int val )
public BigDecimal ( String val )
add
subtract
multiply
divide
// BigDecimal转double
double b = b1 . add ( b2 ). doubleValue ();
// 四舍五入
b1 . divide ( b2 , len , BigDecimal . ROUND_HALF_UP );
前缀和
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// 一维前缀和
S [ i ] = S [ i - 1 ] + a [ i ] ; // 下标从1开始
a [ l ... r ] = S [ r ] - S [ l - 1 ] ;
// 二维前缀和
S [ i ][ j ] = S [ i - 1 ][ j ] + S [ i ][ j - 1 ] - S [ i - 1 ][ j - 1 ] + a [ i ][ j ] ;
a [ x1 .. x2 ][ y1 .. y2 ] = S [ x2 ][ y2 ] - S [ x1 - 1 ][ y2 ] - S [ x2 ][ y1 - 1 ] + S [ x1 - 1 ][ y1 - 1 ] ;
差分
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
/*
初始:
前缀和: 0 0 0 0 0
差分: 0 0 0 0 0
*/
public static void insert ( int l , int r , int c ) {
a [ l ] += c ;
if ( r < n ) a [ r + 1 ] -= c ; // 下标从1开始
}
/*
二维差分
*/
public static void insert ( int l1 , int r1 , int l2 , int r2 , int c ) {
b [ l1 ][ r1 ] += c ;
if ( l2 < n ) b [ l2 + 1 ][ r1 ] -= c ;
if ( r2 < m ) b [ l1 ][ r2 + 1 ] -= c ;
if ( l2 < n && r2 < m ) b [ l2 + 1 ][ r2 + 1 ] += c ;
}
双指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// 暴力 --- 优化
/*
暴力:o(n^2)
优化:o(n) / o(logn) / o(nlogn)
*/
for ( int i = 0 , j = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) {
while ( j <= i && check ( i , j )) {
// ...
}
}
位运算
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
/*
求n的低=第k位数:(n >> k) & 1
返回n的最后一位1:x & -x
lowbit:截取数字中最后一个1后面的所有位
*/
// 计算1的个数
public static int lowbit ( int x ) {
int cnt = 0 ;
while ( x > 0 ) {
int t = x & ( - x );
x -= t ;
cnt ++ ;
}
return cnt ;
}
离散化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
/*
list通过流去重排序
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
list = list.stream().distinct().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
*/
// 映射采用二分,暴力会超时
区间合并
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
/*
想清楚情况:
i: |------|
|--|
|-----|
|-----|
*/
// 依据左端点排序
Arrays . sort ( arr , ( a , b ) -> a [ 0 ] - b [ 0 ] );
// 计算
int l = a [ 0 ][ 0 ] , r = a [ 0 ][ 1 ] ;
for ( int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++ ) {
if ( a [ i ][ 0 ] > r ) {
list . add ( new int [] { l , r });
l = a [ i ][ 0 ] ;
r = a [ i ][ 1 ] ;
} else {
r = Math . max ( r , a [ i ][ 1 ] );
}
}
list . add ( new int [] { l , r });
链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
// 单链表
public static void addHead ( int x ) {
e [ idx ] = x ;
ne [ idx ] = h ;
h = idx ++ ;
}
public static void add ( int k , int x ) {
e [ idx ] = x ;
ne [ idx ] = ne [ k ] ;
ne [ k ] = idx ++ ;
}
public static void delete ( int k ) {
ne [ k ] = ne [ ne [ k ]] ;
}
// 双链表
public static void add ( int k , int x ) {
e [ idx ] = x ;
r [ idx ] = r [ k ] ;
l [ idx ] = k ;
l [ r [ idx ]] = idx ;
r [ k ] = idx ++ ;
}
public static void delete ( int k ) {
r [ l [ k ]] = r [ k ] ;
l [ r [ k ]] = l [ k ] ;
}
栈和队列
单调栈和单调队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// 单调队列
int [] q = new int [ n ] ;
int h = 0 , t = - 1 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) {
// 队头是否移出
if ( h <= t && i - k + 1 > q [ h ] ) h ++ ;
while ( h <= t && a [ q [ t ]] >= a [ i ] ) t -- ;
q [++ t ] = i ;
if ( i >= k - 1 ) {
bw . write ( a [ q [ h ]] + " " );
}
}
KMP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
// 从0开始(不推荐)
// next
int [] next = new int [ n ] ;
next [ 0 ] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 1 , j = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) {
while ( j > 0 && p [ i ] != p [ j ] ) j = next [ j - 1 ] ;
if ( p [ i ] == p [ j ] ) j ++ ;
next [ i ] = j ; // 此时的j是可以匹配的或者0
}
// kmp
for ( int i = 0 , j = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ) {
while ( j > 0 && s [ i ] != p [ j ] ) {
j = next [ j - 1 ] ;
}
if ( s [ i ] == p [ j ] ) j ++ ;
if ( j == n ) {
bw . write ( i - n + 1 + " " );
j = next [ j - 1 ] ;
}
}
// 从1开始
// next
int [] ne = new int [ n + 1 ] ;
ne [ 1 ] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 2 , j = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) {
while ( j > 0 && p [ i ] != p [ j + 1 ] ) j = ne [ j ] ;
if ( p [ i ] == p [ j + 1 ] ) j ++ ;
ne [ i ] = j ; // 此时的j是可以匹配的或者0
}
// kmp
for ( int i = 1 , j = 0 ; i <= m ; i ++ ) {
// 匹配失败,j后退
while ( j > 0 && s [ i ] != p [ j + 1 ] ) j = ne [ j ] ;
// 匹配下一个
if ( s [ i ] == p [ j + 1 ] ) j ++ ;
// 匹配成功
if ( j == n ) {
bw . write ( i - n + " " );
j = ne [ j ] ;
}
}
Tire
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public static void insert ( String s ) {
int p = 1 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < s . length (); i ++ ) {
int x = s . charAt ( i ) - 'a' + 1 ;
if ( son [ p ][ x ] == 0 ) son [ p ][ x ] = ++ idx ;
p = son [ p ][ x ] ;
}
cnt [ p ] ++ ;
}
public static int query ( String s ) {
int p = 1 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < s . length (); i ++ ) {
int x = s . charAt ( i ) - 'a' + 1 ;
if ( son [ p ][ x ] == 0 ) return 0 ;
p = son [ p ][ x ] ;
}
return cnt [ p ] ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
class Trie {
private Trie [] son ;
private boolean isEnd ;
public Trie () {
son = new Trie [ 26 ] ;
isEnd = false ;
}
public void insert ( String word ) {
Trie p = this ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < word . length (); i ++ ) {
int idx = word . charAt ( i ) - 'a' ;
if ( p . son [ idx ] == null ) {
p . son [ idx ] = new Trie ();
}
p = p . son [ idx ] ;
}
p . isEnd = true ;
}
public boolean search ( String word ) {
Trie p = searchWord ( word );
return p == null ? false : p . isEnd ;
}
public boolean startsWith ( String prefix ) {
Trie p = searchWord ( prefix );
return p != null ;
}
public Trie searchWord ( String s ) {
Trie p = this ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < s . length (); i ++ ) {
int idx = s . charAt ( i ) - 'a' ;
if ( p . son [ idx ] == null ) return null ;
p = p . son [ idx ] ;
}
return p ;
}
}
并查集
1
2
3
4
public static int find ( int x ) {
if ( p [ x ] != x ) p [ x ] = find ( p [ x ] );
return p [ x ] ;
}
堆
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
public static void swap ( int i , int j ) {
// 1.交换ph指针
int t = ph [ hp [ i ]] ;
ph [ hp [ i ]] = ph [ hp [ j ]] ;
ph [ hp [ j ]] = t ;
// 2.交换hp指针
t = hp [ i ] ;
hp [ i ] = hp [ j ] ;
hp [ j ] = t ;
// 3.交换值
t = a [ i ] ;
a [ i ] = a [ j ] ;
a [ j ] = t ;
}
public static void down ( int k ) {
int t = k ;
if ( 2 * k <= size && a [ 2 * k ] < a [ t ] ) t = 2 * k ;
if ( 2 * k + 1 <= size && a [ 2 * k + 1 ] < a [ t ] ) t = 2 * k + 1 ;
if ( k != t ) {
swap ( k , t );
down ( t );
}
}
public static void up ( int k ) {
while ( k / 2 > 0 && a [ k / 2 ] > a [ k ] ) {
swap ( k / 2 , k );
k /= 2 ;
}
}
哈希表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// 开发寻址
public static int find ( int x ) {
int k = ( x % N + N ) % N ;
while ( h [ k ] != NULL && h [ k ] != x ) {
k ++ ;
if ( k == N ) k = 0 ;
}
return k ;
}
// 拉链法
public static void insert ( int x ) {
int n = ( x % N + N ) % N ; // 求非负余数而非余数取正,故不是abs
// 头插法
e [ idx ] = x ; ne [ idx ] = h [ n ] ; h [ n ] = idx ++ ;
}
public static boolean query ( int x ) {
int n = ( x % N + N ) % N ;
for ( int i = h [ n ] ; i != - 1 ; i = ne [ i ] ) {
if ( e [ i ] == x ) return true ;
}
return false ;
}
DFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public void dfs ( int k ) {
if ( k == n ) {
// ...
}
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) {
if ( ! st [ i ] ) {
// g[k] = i;
st [ i ] = true ;
dfs ( k + 1 ); // 前后恢复现场
st [ i ] = false ;
}
}
}
BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public int bfs ( int k ) {
Queue < Integer > q = new LinkedList <> ();
// 初始化...
while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) {
int t = q . poll ();
// 拓展t...
}
}
深度优先遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public int dfs ( int k ) {
st [ k ] = true ;
for ( int i = h [ k ] ; i != - 1 ; i = ne [ i ] ) {
int j = e [ i ] ;
if ( ! st [ j ] ) {
// ...
dfs ( j );
}
}
}
广度优先遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public int bfs () {
Queue < Integer > q = new LinkedList <> ();
q . offer ( 1 );
d [ 1 ] = 0 ; /* st[1] = true; */
while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) {
int t = q . poll ();
for ( int i = h [ t ] ; i != - 1 ; i = ne [ i ] ) {
int j = e [ i ] ;
if ( d [ j ] == - 1 /* !st[j] */ ) {
d [ j ] = d [ t ] + 1 ; /* st[j] = true; */
q . offer ( j );
}
}
}
return d [ n ] ;
}
拓扑排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public boolean topSort () {
Queue < Integer > q = new LinkedList <> ();
// 将所有入度为0的点加入队列
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) {
// d[i] 表示i节点的入度有几个
if ( d [ i ] == 0 ) {
q . offer ( i );
}
}
while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) {
int t = q . poll ();
g [ cnt ++] = t ;
for ( int i = h [ t ] ; i != - 1 ; i = ne [ i ] ) {
int j = e [ i ] ;
d [ j ]-- ; // 先删去当前的关系,不为0说明还有其他点指向当前的点
if ( d [ j ] == 0 ) {
q . offer ( j );
}
}
}
// 所有点都进入结果数组了,说明存在;否则不存在
return cnt == n ;
}
Dijkstra
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public int dijkstra () {
Arrays . fill ( d , INF );
d [ 0 ] = 1 ;
// 遍历n次,每次加入一个点
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) {
// 1.找到S中不存在且距离最短的点t
int t = - 1 ;
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ ) {
if ( ! st [ j ] && ( t == - 1 || d [ t ] > d [ j ] )) {
t = j ;
}
}
// 2.将t加入S中
st [ t ] = true ;
// 3.通过t更新其他点到起点的距离
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ ) {
d [ j ] = Math . min ( d [ j ] , d [ t ] + g [ t ][ j ] );
}
}
// 返回结果,若为INF表示无法达到
return d [ n ] == INF ? - 1 : d [ n ] ;
}
Bellman-ford
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
class Edge {
int a , int b , int w ;
public Edge ( int a , int b , int w ) {
this . a = a ;
this . b = b ;
this . w = w ;
}
}
public static int bellmanFord () {
Arrays . fill ( d , INF );
d [ 1 ] = 0 ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < k / n ; i ++ ) {
db = Arrays . copyOf ( d , N ); // 备份,防止串联修改
for ( int j = 0 ; j < m ; j ++ ) { // 遍历所有边
int a = edges [ j ] . a , b = edges [ j ] . b , w = edges [ j ] . w ;
d [ b ] = Math . min ( d [ b ] , db [ a ] + w );
}
}
return d [ n ] > INF / 2 ? - 1 : d [ n ] ;
}
// INF / 2
Spfa
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public int spfa () {
Queue < Integer > q = new LinkedList <> ();
q . offer ( 1 );
Arrays . fill ( d , INF );
d [ 1 ] = 0 ;
st [ 1 ] = true ; // 判断点是否在队列中
while ( ! q . isEmpty ()) {
int t = q . poll ();
st [ t ] = false ;
for ( int i = h [ t ] ; i != - 1 ; i = ne [ i ] ) {
int j = e [ i ] ;
if ( d [ j ] > d [ t ] + w [ i ] ) { // 只有当d[t]减小时,d[j]才有可能减小
d [ j ] = d [ t ] + w [ i ] ;
if ( ! st [ j ] ) {
st [ j ] = true ;
q . offer ( j );
}
}
}
}
return d [ n ] > INF ? - 1 : d [ n ] ;
}
Floyd
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
// 初始化
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ ) {
if ( i == j ) d [ i ][ j ] = 0 ;
else d [ i ][ j ] = INF ;
}
}
public void floyd () {
for ( int k = 1 ; k <= n ; k ++ ) {
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ ) {
d [ i ][ j ] = Math . min ( d [ i ][ j ] , d [ i ][ k ] + d [ k ][ j ] );
}
}
}
}
// INF / 2
Prim
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public int prim () {
Arrays . fill ( d , INF );
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) {
// 找到不在s中且距离最近的点
int t = - 1 ;
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ ) {
if ( ! st [ j ] && ( t == - 1 || d [ j ] < d [ t ] )) {
t = j ;
}
}
// 判断是否有连通
if ( i != 0 && d [ t ] = INF ) return INF ;
if ( i != 0 ) res += d [ t ] ;
// 加入点
st [ t ] = true ;
// 根据点修改其他点到集合的距离
for ( int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ ) {
d [ j ] = Math . min ( d [ j ] , g [ t ][ j ] );
}
}
}
Kruskal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
class Edge {
int u , int v , int w ;
public Edge ( int u , int v , int w ) {
this . u = u ;
this . v = v ;
this . w = w ;
}
}
public int kruskal () {
// 将所有边按照权重升序
Arrays . sort ( edges , ( a , b ) -> a . w - b . w );
// 枚举每条边,没连通加入
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) {
int u = edges [ i ] . u , v = edges [ i ] . v , w = edges [ i ] . w ;
int fu = find ( u ), fv = find ( fv );
if ( fu != fv ) {
p [ fu ] = fv ;
res += w ;
cnt ++ ;
}
}
// 确保连通
if ( cnt < n - 1 ) return - 1 ;
else return res ;
}
// 并查集的find函数
染色法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// dfs or bfs
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) {
if ( color [ i ] == 0 ) {
if ( ! dfs ( i , 1 )) {
flag = false ;
break ;
}
}
}
if ( flag ) ...;
else ...;
public static boolean dfs ( int k , int c ) {
color [ k ] = c ;
for ( int i = h [ k ] ; i != - 1 ; i = ne [ i ] ) {
int j = e [ i ] ;
if ( color [ j ] == 0 ) {
if ( ! dfs ( j , 3 - c )) return false ;
} else if ( color [ j ] == c ) return false ;
}
return true ;
}
匈牙利算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// 邻接表 or 邻接绝阵
for ( int i = 1 ; i <= n1 ; i ++ ) {
Arrays . fill ( st , false );
if ( find ( i )) res ++ ;
}
public boolean find ( int k ) {
for ( int i = h [ k ] ; i != - 1 ; i = ne [ i ] ) {
int j = e [ i ] ;
if ( ! st [ j ] ) {
st [ j ] = true ;
if ( match [ j ] == 0 || find ( match ( j ))) {
match [ j ] = k ;
return true ;
}
}
}
return false ;
}
数学知识
欧拉函数
1~N中与N互质的数的个数被称为欧拉函数,记为ϕ(N)
若在算数基本定理中,N = p1^a1^p2^a2^ … pm^am^
$$
ϕ(N) = N * \frac{p_1 - 1}{p_1} * \frac{p_2 - 1}{p_2} * ... * \frac{p_m - 1}{p_m}
$$
乘法逆元
若整数 b,m 互质,并且对于任意的整数 a,如果满足 b|a,则存在一个整数 x,使得 a / b = a * x (mod m)
则称 x 为 b 的模 m 乘法逆元,记为b^-1^ (mod m)
b 存在乘法逆元的充要条件是 b 与模数 m 互质。当模数m为质数时,b^m-2^ 即为 b 的乘法逆元
欧几里得算法
gcd
费马小定理
如果p是一个质数,而整数a不是p的倍数,则有
$$
a^{p - 1} \equiv 1 \ (mod \ p)
$$
裴蜀定理 —> 扩展欧几里得算法
对于任意正整数 a,b,一定存在非零整数 x,y 使得 ax + by = (a, b) (a,b的最大公约数)
ax0 + by0 = d
通解:
$$
\begin{cases}
x = x_0 - k * \frac{b}{d} \\
y = y_0 + k * \frac{a}{d}
\end{cases}
$$
中国剩余定理
设正整数 m1,m2 … ,mk,两两互质,则同余方程组:
$$
\begin{cases}
x \equiv a_1 \ (\ mod \ m_1 \ ) \\
x \equiv a_2 \ (\ mod \ m_2 \ ) \\
... \\
x \equiv a_k \ (\ mod \ m_k \ )
\end{cases}
$$
有整数解,并且在模 M = m1 * m2 * … * mk 下的解是唯一的,解为
$$
x \equiv (a_1M_1M_1^{-1} + a_2M_2M_2^{-1} + \ ... \ + a_kM_kM_k^{-1}) \ mod \ M
$$
其中Mi = M / mi,Mi^-1^ 表示 Mi 模 mi 的逆元
扩展欧几里得算法
质数
判断质数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public boolean isPrime ( int x ) {
if ( x <= 1 ) return false ;
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= x / i ; i ++ ) {
if ( x % i == 0 ) return false ;
}
return true ;
}
分解质因数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public void divide ( int x ) {
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= x / i ; i ++ ) {
if ( x % i == 0 ) {
int t = 0 ;
while ( x % i == 0 ) {
t ++ ;
x /= i ;
}
System . out . println ( i + " " + t );
}
if ( m > 1 ) System . out . println ( m + " " + 1 );
System . out . println ( "" );
}
}
筛质数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
// 朴素法
// 会重复筛
public int getPrimes ( int n ) {
int cnt = 0 ;
int [] primes = new int [ n + 1 ] ;
boolean [] st = new boolean [ n + 1 ] ;
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) {
if ( ! st [ i ] ) {
st [ i ] = true ;
primes [ cnt ++] = i ;
for ( int j = i + i ; j <= n ; j += i ) {
st [ j ] = true ;
}
}
}
return cnt ;
}
// 线性法
public int getPrimes ( int n ) {
int cnt = 0 ;
int [] primes = new int [ n + 1 ] ;
boolean [] st = new boolean [ n + 1 ] ;
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) {
if ( ! st [ i ] ) primes [ cnt ++] = i ;
for ( int j = 0 ; primes [ j ] <= n / i ; j ++ ) {
st [ primes [ j ] * i ] = true ;
if ( i % primes [ j ] == 0 ) break ;
}
}
return cnt ;
}
约数
求约数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public List < Integer > getDivisors ( int x ) {
List < Integer > list = new ArrayList <> ();
for ( int i = 0 ; i <= m / i ; i ++ ) {
if ( m % i == 0 ) {
list . add ( i );
}
// 去重
if ( i != m / i ) list . add ( m / i );
}
// 排序
list . sort ( Comparator . naturalOrder ());
return list ;
}
约束个数 & 约束之和
N = p1^a1^ * p2^a2^ * … * pk^ak^
约数个数:(a1 + 1) * (a2 + 1) * … * (ak + 1)
约数之和:(p1^0^ + p1^1^ + … + p1^a1^) * (p2^0^ + p2^1^ + … + p2^a2^) * … * (pk^0^ + pk^1^ + … + pk^ak^)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Map < Integer , Integer > map = new HashMap <> ();
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) {
int m = Integer . parseInt ( br . readLine ());
for ( int j = 2 ; j <= m / j ; j ++ ) {
if ( m % j == 0 ) {
int t = 0 ;
while ( m % j == 0 ) {
t ++ ;
m /= j ;
}
map . put ( j , map . getOrDefault ( j , 0 ) + t );
}
}
if ( m > 1 ) map . put ( m , map . getOrDefault ( m , 0 ) + 1 );
}
最大公约数(欧几里得算法 / 辗转相除法)
1
2
3
4
// a > b
public int gcd ( int a , int b ) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd ( b , a % b );
}
欧拉函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
long res = n ;
for ( int i = 2 ; i <= n / i ; i ++ ) {
if ( m % i == 0 ) {
res = res / i * ( i - 1 );
while ( m % j == 0 ) m /= j ;
}
if ( m > 1 ) res = res / m * ( m - 1 );
}
快速幂
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// a^b
public long qmi ( int a , int b ) {
long res = 1 ;
while ( b > 0 ) {
if (( b & 1 ) == 1 ) res *= a ;
a *= a ;
b >> 1 ;
}
return res ;
}
扩展欧几里得算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// 求 x, y
// a * x + b * y = gcd(a, b)
public int exgcd ( int a , int b , int [] result ) {
if ( b == 0 ) {
result [ 0 ] = 1 ;
result [ 1 ] = 0 ;
return a ;
}
int d = exgcd ( b , a % b , result );
int t = result [ 0 ] ;
result [ 0 ] = result [ 1 ] ;
result [ 1 ] = t - a / b * result [ 1 ] ;
return d ;
}
中国剩余定理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
import java.util.* ;
import java.io.* ;
public class Main {
public static void main ( String [] args ) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader ( new InputStreamReader ( System . in ));
int n = Integer . parseInt ( br . readLine ());
String [] s = br . readLine (). split ( " " );
long a1 = Integer . parseInt ( s [ 0 ] );
long m1 = Integer . parseInt ( s [ 1 ] );
// 用于标记是否有解,初始化为 true
boolean hasAnswer = true ;
while ( n -- > 1 ) {
s = br . readLine (). split ( " " );
long a2 = Integer . parseInt ( s [ 0 ] );
long m2 = Integer . parseInt ( s [ 1 ] );
long [] result = new long [ 2 ] ;
long d = exgcd ( a1 , a2 , result );
if (( m2 - m1 ) % d != 0 ) {
hasAnswer = false ;
break ;
}
result [ 0 ] *= ( m2 - m1 ) / d ;
long t = a2 / d ;
result [ 0 ] = ( result [ 0 ] % t + t ) % t ;
m1 = result [ 0 ] * a1 + m1 ;
a1 = Math . abs ( a1 / d * a2 );
}
if ( hasAnswer ) {
System . out . println (( m1 % a1 + a1 ) % a1 );
} else {
System . out . println ( "-1" );
}
}
public static long exgcd ( long a , long b , long [] result ) {
if ( b == 0 ) {
result [ 0 ] = 1 ;
result [ 1 ] = 0 ;
return a ;
}
long d = exgcd ( b , a % b , result );
long t = result [ 0 ] ;
result [ 0 ] = result [ 1 ] ;
result [ 1 ] = t - a / b * result [ 1 ] ;
return d ;
}
}
高斯消元
求组合数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// 从 a 个苹果中选 b 个苹果
// 从 i 个苹果中选 j 个苹果
int c [ N ][ N ] ;
public void init () {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ )
for ( int j = 0 ; j <= i ; j ++ )
if ( j == 0 ) c [ i ][ j ] = 1 ;
else c [ i ][ j ] = ( c [ i - 1 ][ j ] + c [ i - 1 ][ j - 1 ] ) % mod ;
}
容斥原理
博弈论
数据结构
String:字符串
String s = “aabccabcd”
s.charAt(2); // ‘b’
s.concat(“hello”); // “aabccabcdhello”
s.startsWith(“hello”); // 判断字符是否以"hello"开头
s.endsWith(“hello”); // 判断字符是否以"hello"结尾
s.equals(“aaaaa”); // 判断字符串是否相等
s.equalsIgnoreCase(“aaaa”); // 忽略大小写比较是否相等
s.getBytes(); // 将字符串转化为字节数组
s.length(); // 返回此字符串的长度
s.replace(‘a’, ‘f’); // 将字符串中所有的’a’替换为’f’
s.split(" “); // 将字符串以空格作为分隔符,转化为字符串数组
s.substring(1); // 返回索引从1开始的字符串(索引从 0 开始)
s.substring(1, 4); // 返回从索引1开始,到4结束(不包括4)的字符串
s.tocharArray(); // 将字符串转化为字符数组
s.toLowerCase(); // 将字符串中的所有字符都转换为小写
s.toUpperCase(); // 将字符串中的所有字符都转换为大写
s.trim(); // 删除头尾空白
s.contains(“aa”); // 判断字符串中是否包含指定的字符或字符串
s.isEmpty(); // 判断字符串是否为空
ArrayList
List list = new ArraysList<>();
List list2 = new ArraysList<>();
list.add(“aaa”); // 直接添加元素
list.add(0, “aaa”); // 通过索引添加元素
list.addAll(list2); // 添加list2所有元素到list
List list3 = new ArraysList<>(Arrays.asList(“aaa”, “bbb”, “ccc”));
list.get(0); // 通过索引访问list中的元素
list.remove(2); // 通过索引删除list中的元素
list.clear(); // 清空list数组
list.size(); // 返回list中的元素个数
for / for-each // 遍历list
Collection.sort(list); // 对list进行排序
String[] arr = new String[list.size()];
list.toArray(arr); // 将list转化为数组
List list4= new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(arr)); //从数组创建ArrayList
list.toString(); // 将list转化为字符串
list.isEmpty(); // 判断list是否为空
list.contains(“aaa”); // 判断list中是否存在指定元素
list.indexOf(“aaa”); // 查找"aaa"的所在索引,不存在返回-1
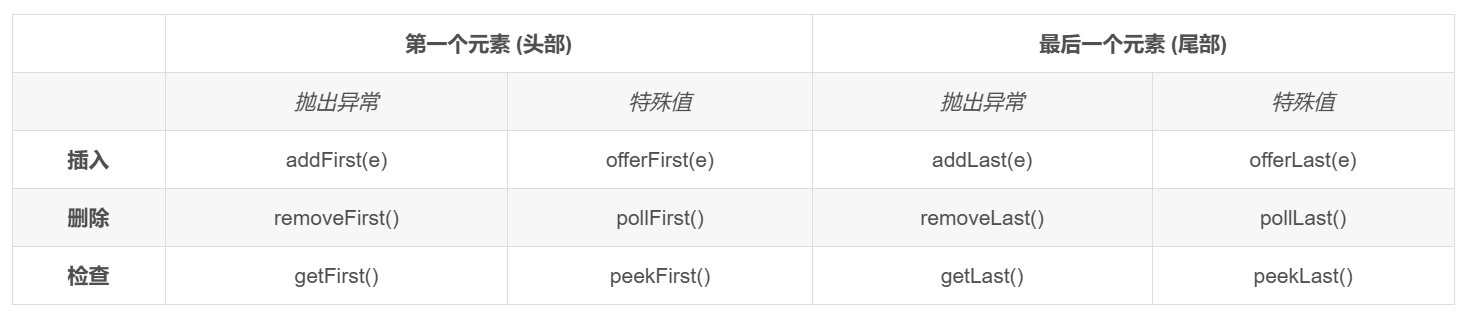
Deque
PriorityQueue(堆)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
// 创建小根堆
PriorityQueue < Integer > minHeap = new PriorityQueue <> (( a , b ) -> a - b );
// 加入数据
minHeap . offer ( 3 ); // add
minHeap . offer ( 1 );
minHeap . offer ( 4 );
minHeap . offer ( 1 );
minHeap . offer ( 5 );
// 不断取出最小值
while ( ! minHeap . isEmpty ()) {
int cur = minHeap . poll (); // int
System . out . println ( cur + " " );
}
// 1 1 3 4 5
// 其他方法
minHeap . peek ();
minHeap . remove ( int x ); // boolean
// 遍历
Iterator < Integer > iterate = minHeap . iterator ();
while ( iterate . hasNext ()) {
System . out . print ( iterate . next () + " " );
}
// 比较器
PriorityQueue < Integer > numbers = new PriorityQueue <> ( new CustomComparator ());
class CustomComparator implements Comparator < Integer > {
@Override
public int compare ( Integer n1 , Integer n2 ) {
if ( n1 > n2 ) return - 1 ;
else if ( n1 < n2 ) return 1 ;
else return 0 ;
}
}
Arrays
Arrays.fill(arr, data); # 填充数组
Arrays.sort(); # 数组排序
1
2
3
4
5
Arrays . sort ( int [][] arr , new Comparator < int []> () {
public int compare ( int [] p1 , int [] p2 ) {
return p1 [ 1 ]- p2 [ 1 ] ;
}
});
Arrays.toString(arr); # 将数组中的内容全部打印出来
Arrays.equals(arr1, arr2); # 比较数组元素是否相等
Arrays.binarySearch(arr, data); # 二分查找法找指定元素的下标
Arrays.copeOf(arr, len); # 截取数组
Arrays.copeOfRange(arr, left, right);
时间复杂度
Licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0